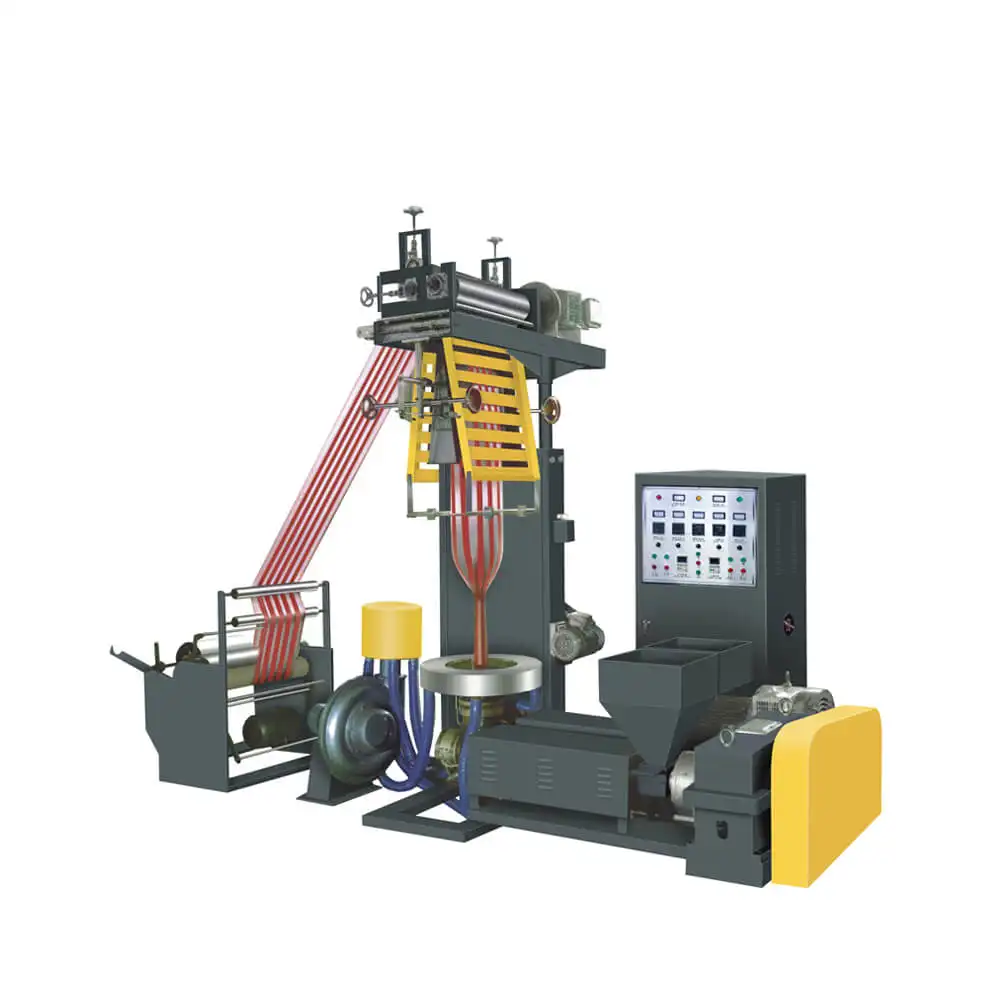
ABA Film Blowing Machine: This ABA Film Blowing Machine revolutionizes flexible packaging production with advanced co-extrusion technology. These systems consist of two extruders, one central for the core layer (B) and one lateral for the two outer layers (A). The die on the machine has two flow channels instead of one, so polymer flow can be accurately regulated for both sides of the symmetrical exterior shells surrounding the core structure.
This configuration enables manufacturers to optimize layer thickness ratios, balancing performance and cost. For instance, the B-layer often incorporates cost-saving fillers like calcium carbonate (up to 50%), reducing virgin polymer use by 30% while maintaining strength.
The ABA trilayer structure is ideal for applications requiring stiffness and puncture resistance, such as industrial liners and agricultural films. Modern systems also integrate recycled content in outer layers without compromising printability—a critical advantage for brands pursuing sustainability targets.
The ABA Trilayer Structure: Foundation for Blowing Film Machine Strength

Layer Composition in Co-Extrusion Film Production
The ABA trilayer configuration consists of three polymer layers which are co-extrusion blown film extruded. The outer layers (A) are generally made from virgin polymers, for example HDPE or LDPE, for quality of surface, whereas the core layer (B) contains inexpensive materials, such as recoverable plastics or calcium carbonate based composites. The second structure offers an 18–22% lower raw material cost compared to single layer films, and is most preferred when the layer ratio is set at 10:80:10--20:60:20 (A:B:A).
Material Selection for Barrier and Structural Layers
Barrier layers use polymers with low gas permeability (e.g., EVOH or nylon), while structural layers prioritize impact-resistant resins like LLDPE. Studies show blending up to 50% calcium carbonate in the B-layer reduces virgin material consumption by 34% while maintaining tensile strength.
Interfacial Adhesion in Multilayer Films
Thermal compatibility between layers ensures strong adhesion. Modern systems maintain melt temperature differentials within 15°C to prevent delamination, achieving adhesion strength exceeding 4.5 N/15mm.
Production Advantages of Co-Extrusion Blowing Machines
Simultaneous Processing of Multiple Polymers
Modern co-extrusion systems integrate up to seven polymer layers in a single pass, eliminating secondary lamination. Manufacturers achieve 23% faster production cycles compared to monolayer film processing.
Energy Efficiency in Co-Extrusion Processing
Co-extrusion reduces energy consumption by 18-32% through single-heat-cycle processing, scrap minimization, and precise temperature control.
Enhancing Mechanical Properties in Blown Films
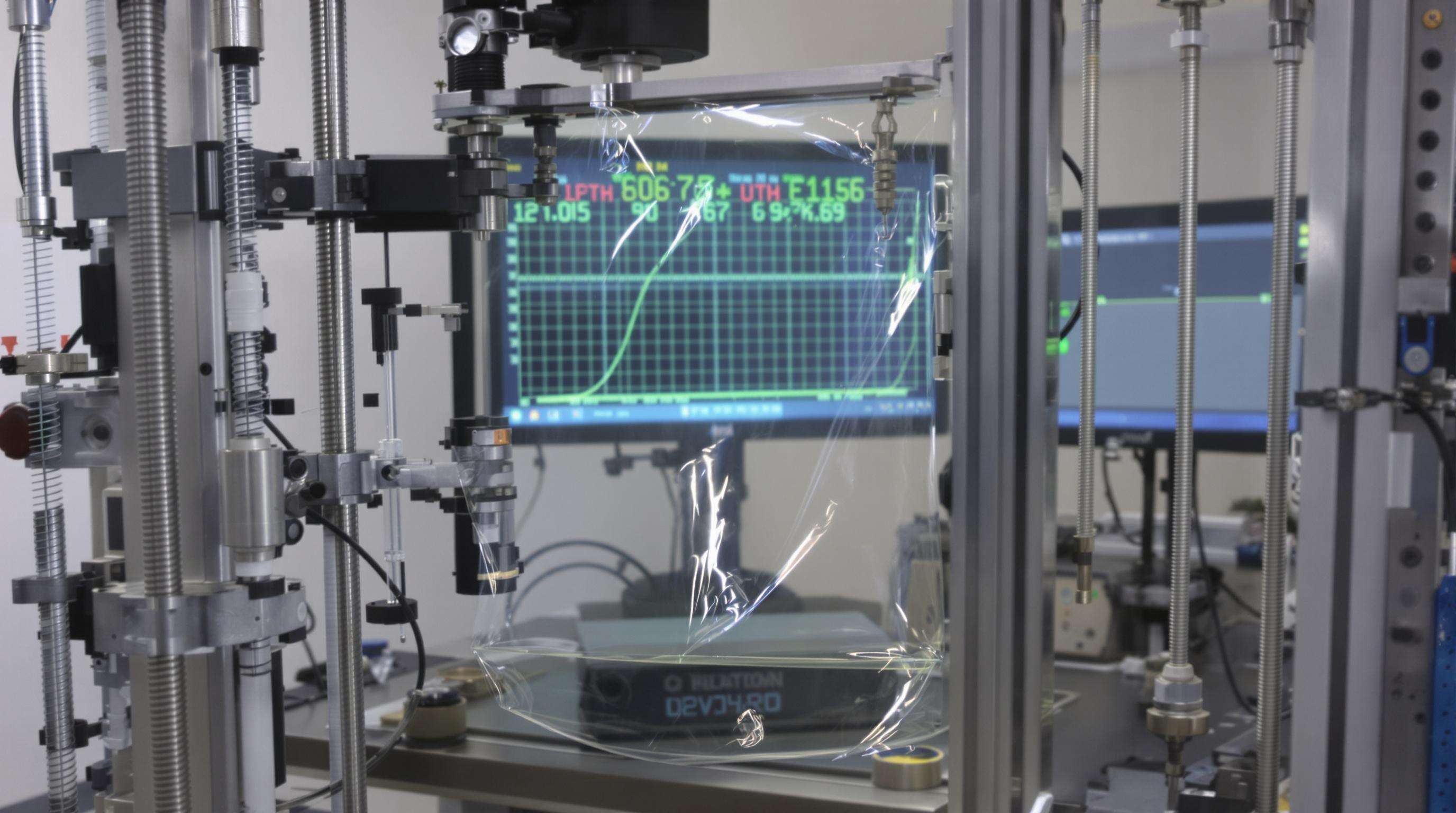
Stress Distribution in Multilayer Film Architecture
The ABA trilayer structure optimally distributes mechanical stresses. Simulations show 40% more uniform stress distribution in 3-layer films versus single-layer equivalents.
Impact Resistance Through Layer Optimization
Films with optimized layer ratios withstand up to 2.3" higher puncture forces, enabled by real-time thickness monitoring (±5% consistency).
Case Study: 23% Tear Strength Improvement (2023 FIAP Data)
| Parameter | Baseline (2-Layer) | Optimized 3-Layer | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tear Resistance (N/mm) | 32.4 | 39.8 | 23% |
Flexible Packaging Applications of High-Strength Films
Heavy-Duty Industrial Bag Solutions
Co-extruded HDPE/LLDPE blends withstand 500+ compression cycles, enabling 50 kg bulk bags with 40% thinner walls.
Puncture-Resistant Food Packaging Films
Multilayer films achieve 300% higher puncture resistance, extending meat and seafood shelf life by 8–12 days.
Lightweighting Trends in Consumer Packaging
| Property | Traditional Film | Advanced ABA Film |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 35μm | 22μm (-37%) |
| Carbon Footprint | 1.8 kg CO2/kg | 1.2 kg CO2/kg (-33%) |
Sustainability Considerations in Plastomer Processing
Recyclability Challenges in Co-Extruded Films
Only 32% of co-extruded films are recovered for reuse due to polymer incompatibility, compared to 58% for mono-material alternatives.
Bio-Based Material Integration Strategies
PLA now accounts for 12% of structural layers in European food packaging, offering a 40% lower GHG footprint than PE.
Industry Paradox: Performance vs. Circular Economy Demands
While 73% of converters prioritize mechanical performance, regulations require ≥35% recycled content by 2025. Emerging hybrid systems achieve 91% of virgin material performance while meeting recyclability thresholds.
Adding compatibilizers during production can improve recyclate purity by up to 19%.
2023 industry analysis revealed challenges in balancing recycled content with performance.
FAQ
What is an ABA Film Blowing Machine?
An ABA Film Blowing Machine features advanced co-extrusion technology and consists of two extruders for creating a trilayer film with specific layer thickness ratios for better performance and cost-effectiveness.
What materials are used in ABA blown films?
The outer layers are typically made of virgin polymers like HDPE or LDPE, while the core layer can include inexpensive materials such as calcium carbonate or recoverable plastics.
What are the sustainability considerations for co-extruded films?
Sustainability concerns include recyclability challenges due to polymer incompatibility and exploring bio-based material integration for a reduced carbon footprint.




